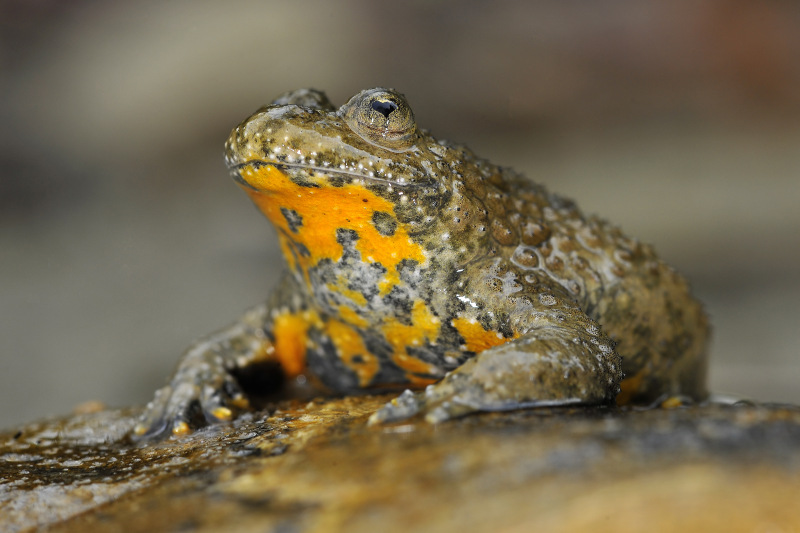
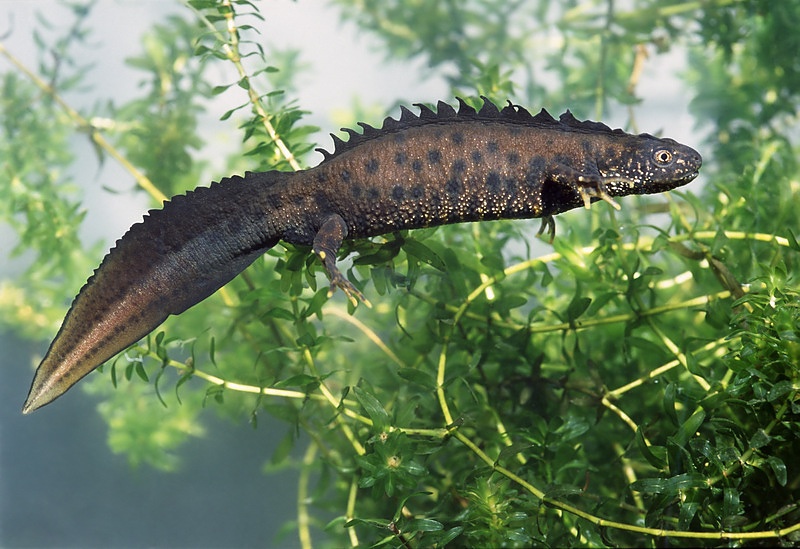
Amphibians and reptiles are vertebrates with a variable body temperature. Amphibians are dependent on the availability of water for reproduction and, in some cases, for habitat. For this, they prefer shady valleys, northern slopes, marshy meadows and other wet areas. Unlike amphibians, reptiles are significantly more common on sunny, warm slopes overgrown with shrubby or sparse tree vegetation. Representatives of both classes are an important food base for many species of predatory mammals, waterfowl and birds of prey. Their species richness is high considering the geographical position and area of the park. The main prerequisites are the presence of diverse habitats in a wide altitude range (425-1482 m) and the wide occurrence of karst landscapes. 11 species of amphibians (61% of the species in Bulgaria) and 15 species of reptiles (42% of the species in Bulgaria) are found on the territory of the "Vrachanski Balkan" Nature Park.
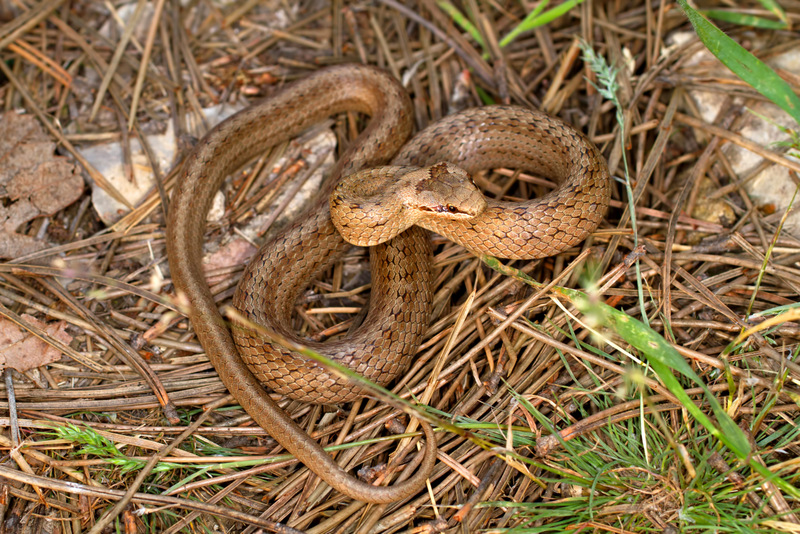

Amphibians are a reliable indicator of the cleanliness of the aquatic environment. Many of the species do not lay eggs or do not hatch into larvae in contaminated with organic waste, nitrogen fertilizers and other agricultural poisons. The absence of amphibians in the aquatic environment during the breeding period (late March-June) is a sure sign of pollution of inorganic or organic origin.
Conservation status
Of the 26 species of amphibians and reptiles established on the territory of the Vrachanski Balkan National Park, 20 are protected under the Law on Biological Diversity. 20 species are protected under Directive 92/43 of the EEC. The habitats of the northern and southern crested newt (Triturus cristatus, Triturus karelinii), the yellow-bellied bumblebee (Bombina variegata), the two species of land turtles (Testudo graeca, Testudo hermanii), as well as the common terrapin (Emys orbicularis) are priorities for conservation according to the Law on biological diversity.
Threats to amphibians and reptiles on the territory of the "Vrachanski Balkan" Nature Park.
- Fires;
- Human activity leading to change or loss of habitats;
- Drying water bodies;
- Roads;
- Threats from the settlement of invasive species;